SOP_data
Standard Operating Procedures
Project maintained by stajichlab Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Amplicon Data Processing using AMPtk
We will use AMPtk to process amplicon data.
We can get this data from a public dataset stored in NCBI. First let’s look at the BioProject page PRJNA379160. This page provides links to the 98 SRA experiments for 16S and ITS amplicon data from Antarctic cryptoendolithic communities.
Although, this study has both 16S and ITS amplicon data, we will perform data processing only on several samples from ITS data. Data are already available on stajichlab UCR HPCC. We will set up our analysis folder using following instructions.
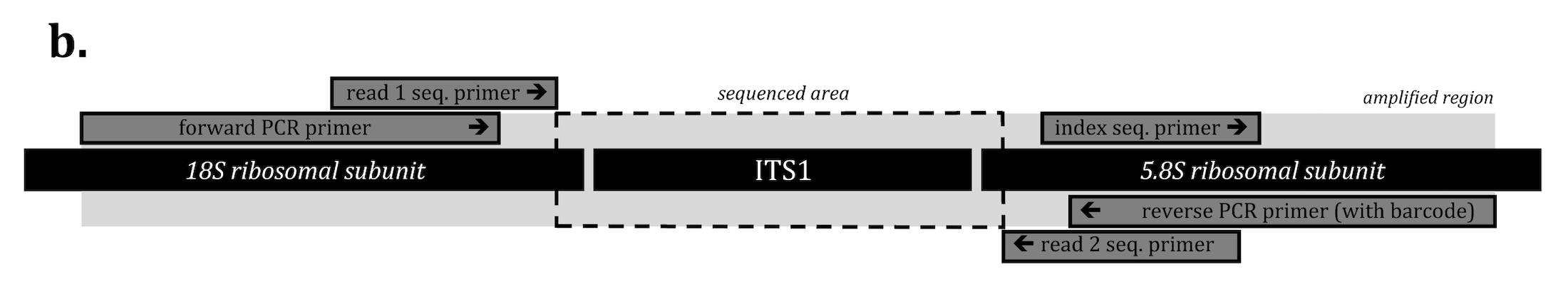
ITS primers for this project contain unique barcode for each sample. We usually submit ~250 samples per illumina miseq run. After sequencing process, the barcodes will be used to split sequences into fastq file for each sample.
Setting up analysis
First make a data folder (illumina) in bigdata to begin your analysis, change directory to illumina, and create symlink to subset of ITS amplicon data.
cd ~/bigdata/
mkdir -p AMPtk/illumina/
cd AMPtk/illumina/
# create a symlink to the datasets
ln -s ~/shared/projects/Microbiome/data/Amplicon_Pipeline/ITS/illumina/*8* .
cd ..
Now, you should have these 10 data files in your illumina folder and you could verify the previous step by simply use ls.
ls illumina/
ITS.CC.18A_R1.fastq.gz ITS.CC.28A_R1.fastq.gz ITS.CC.8B_R1.fastq.gz
ITS.CC.18A_R2.fastq.gz ITS.CC.28A_R2.fastq.gz ITS.CC.8B_R2.fastq.gz
ITS.CC.18B_R1.fastq.gz ITS.CC.28B_R1.fastq.gz
ITS.CC.18B_R2.fastq.gz ITS.CC.28B_R2.fastq.gz
What does the sequence file look like?
zmore illumina/ITS.CC.18A_R1.fastq.gz | head
@ITS.CC.18A_3 M02457:94:000000000-AMC54:1:1102:9850:1616 1:N:0:1 orig_bc=CTAGTTTTACCA new_bc=CTAGATTTGCCA bc_diffs=2
GTAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAGGATCATTACTGAGAGACGGGCTTTTCTCCCCCCCTCTCTTCTCCCCTCTCTTCTTTACCCTCTTTCTTTCTCCCTTTTTTGCTTTTTCCCTCCCGGTTCTCTTCCCCGCCTTCTCCCCCTCTCCCCTCCCCTGCTCGCCTATCTCCCTTTCAACTCTCTTCTTATTTTCTTTTTTCCTTCCTCTCCCTTTCTACACTTTTTCATTTCTTATTTTTTTCTTCTTTTCTCTTTTTTCTTCCCTCCCTCTATATTTTCTCTTCTCTTTTTCCTTCTTTTTCTTGT
+
-868@CC,,CDE-FF>++7;8CF8FF9-C9,,,,,,-,++8,,6,6C,,8@+++,,:CEE9,CC,C,,,,,<C,,,:9C,,C<<,C9E,6,,,,,,,:++,,<,9?,5,,48++++++:,,5<,,,+6+++,5,:38+3+,,,,+6@+++>+,@B++@++,,,77@<A,,,,,36,,,33,,,,,3,,,7,661,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,2,,,,,61,,,,+++++++++3++*1+++2;+2++312+:++)(++*****/********0*/0*)*+*.-/.):***)))1)))).66).
zmore illumina/ITS.CC.18B_R1.fastq.gz | head
@ITS.CC.18B_247 M02457:94:000000000-AMC54:1:1102:9323:1746 1:N:0:1 orig_bc=TAAGGTAAGGTG new_bc=TAAGGTAAGGTG bc_diffs=0
GTAGGTGAACCTGCGGAAGGATCATTACTGAGAGACGGGGTCTTATCGGCCCCACTCTTCACCCATGTCTACTATACCCTGTTGCTTTGGCGGGCCTTCGGGTCTTACCACCCGGGGCTGGTCGGGGCCTTATGCCCCTCGCTCAGCGAGTGCTCGCCAATGACCCTGTCAACTCTGTTCTTAGTGTCCTCTGAGCAACCACACAATAGGTAAAACTTTCAACAACGGATCTCTTGGTTCTGTCATCGATGTAGAACGCAGCCGTCAGGTAAGTTGATCTCTTATGCCTTCTTTTGCTTGT
+
BC<CCFGFFFFFFGGGD@FGGGGDGGFGGGCGC8,CCC7>FFGFEGGC7FFGG>CFFGFFAEFECFCFFGFEGAFCCCFGCFG<EFGGGDFC7C>FCGG++@ECFFFGF9FFE@+=+@FC:FFE7FC@FGGGGFFFFFFG*@:<3>D:*>>:CEFCCECEC:,2?FG,BC;9CFCFDFFEFG9,?,C?CFEG7+22++<BCC*8**;,2+<++++<CFG?7+<**2***:C:<9C>+<::C++:*9:**:**06++1971:*;8E)/*7>*96*2)0<*66*6):*0:).,9)).6?FA5.
AMPtk data processing steps
I created a bash script containing all the general steps from processing Illumina reads to generating OTU table and assigning taxonomy. We’ll call this pipeline script 01_AMPtk_ITS.sh. We’ll practice similar set up as we’ve have done before by keeping all the script in pipeline folder and log files in logs folder.
#create pipeline folder for scripts and logs folder for log files
mkdir -p pipeline/ logs/
You should now check your AMPtk folder to make sure that you have these folders. Once, we have all the data and folders, we can begin STEP1.
ls -F
illumina/ logs/ pipeline/
STEP 1. Pre-processing
There are several different file format that could be generated from Illumina Miseq sequencing (or sequencing centers). We’ll focus on demultiplexed PE reads in whcih all the sequences were splited into separated fastq files for each samples. The general workflow for Illumina demultiplexed PE reads is:
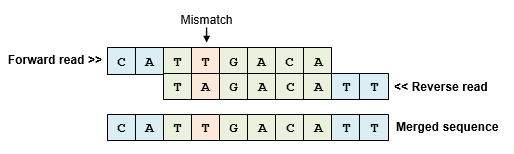
- Merge PE reads (use USEARCH or VSEARCH)
- filter reads that are phiX (USEARCH)
- find forward and reverse primers (pay attention to –require_primer argument)
- remove (trim) primer sequences
- if sequence is longer than –trim_len, truncate sequence
You can use nano editor to simply create 01_AMPtk_ITS.sh script by copyign following command to nano and save the sceript in pipeline folder.
nano pipeline/01_AMPtk_ITS.sh
The beginnings of this script are going to be listed here. You will copy all 4 steps into 01_AMPtk_ITS.sh and run the script.
Note: In this tutorial, we used 10 input files including forward read (_R1) and reverse read (_R2). After the run is completed, we will end up with one big file combining all of the samples and all the _R1 and _R2 will be merged.
#!/usr/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p short -N 1 -n 8 --mem 8gb --out logs/AMPtk_ITS.%a.log
CPU=$SLURM_CPUS_ON_NODE
if [ ! $CPU ]; then
CPU=2
fi
#AMPtk needs to be loaded in miniconda2 for UCR HPCC
#We'll need to unload miniconda3 and load miniconda2 before load AMPtk
module unload miniconda3
module load miniconda2
module load amptk/1.4.0
#Set up basename for all the output that will be generated
BASE=AMPtkITS
#Chnage this to match your data folder name
INPUT=illumina
#Pre-preocessing steps will use `amptk illumia` command for demultiplexed PE reads
if [ ! -f $BASE.demux.fq.gz ]; then
amptk illumina -i $INPUT --merge_method vsearch -f ITS1-F -r ITS2 --require_primer off -o $BASE --usearch usearch9 --cpus $CPU --rescue_forward on --primer_mismatch 2 -l 250
fi
STEP 2. Clustering
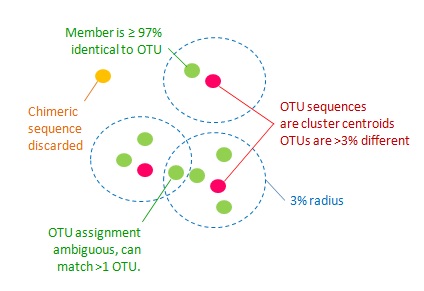
This step will cluster sequences into Operational Taxonomy Unit (OTU), then generate representative OTU sequences and OTU table. OTU generation pipelines in AMPtk uses UPARSE clustering with 97% similarity (this can be changed).
Note: at clustering step, we used merged sequence from STEP1 as an input and we will generate clustered sequences file and OTU table.
if [ ! -f $BASE.otu_table.txt ]; then
amptk cluster -i $BASE.demux.fq.gz -o $BASE --uchime_ref ITS --usearch usearch9 --map_filtered -e 0.9 --cpus 8
fi
Checking OTU table
head AMPtkITS.otu_table.txt
#OTU ID ITS.CC.18A ITS.CC.18B ITS.CC.28A ITS.CC.28B ITS.CC.8B
OTU1 2301 2871 353140 11034 14929
OTU10 0 2580 2 0 0
OTU100 0 3 0 0 0
OTU101 0 0 6 0 0
OTU102 1 0 3 0 1
OTU104 1 0 1 0 0
OTU105 0 2 33 0 0
OTU106 1 0 5 0 1
OTU107 1 0 5 1 1
STEP 3. Taxonomy Assignment
This step will assign taxonomy to each OTU sequence and add taxonomy to OTU table. This command will generate taxnomy based on the ITS database.
Note: at Taxonomy Assignment step, we will use clustered sequences file and OTU table for taxonomy assignment from ITS database
if [ ! -f $BASE.otu_table.taxonomy.txt ]; then
amptk taxonomy -f $BASE.cluster.otus.fa -i $BASE.otu_table.txt -d ITS
fi
When the taxonomy assignment is completed, we can check the taxonmy file which will be AMPtkITS.cluster.taxonomy.txt
head -5 AMPtkITS.cluster.taxonomy.txt
#OTUID taxonomy USEARCH SINTAX UTAX
OTU1 GS|100.0|GU074436|SH1524733.08FU;k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Lecideales,f:Lecideaceae,g:Lecidea,s:Lecidea cancriformis k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Lecideales,f:Lecideaceae,g:Lecidea,s:Lecidea cancriformis k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Lecideales,f:Lecideaceae,g:Lecidea,s:Lecidea cancriformis k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Lecideales,f:Lecideaceae,g:Lecidea
OTU3 US|0.9077|KF823589|SH1564421.08FU;k:Fungi,p:Basidiomycota,c:Tremellomycetes,o:Tremellales k:Fungi,p:Basidiomycota,c:Tremellomycetes,o:Tremellales,f:Sirobasidiaceae k:Fungi k:Fungi,p:Basidiomycota,c:Tremellomycetes,o:Tremellales
OTU4 SS|1.0000|LN810767|SH1614717.08FU;k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Acarosporales,f:Acarosporaceae k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Acarosporales,f:Acarosporaceae,g:Acarospora,s:Acarospora fuscata k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Acarosporales,f:Acarosporaceae k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Acarosporales,f:Acarosporaceae
OTU5 SS|1.0000|LN881898|NA;k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Acarosporales,f:Acarosporaceae k:Fungi k:Fungi,p:Ascomycota,c:Lecanoromycetes,o:Acarosporales,f:Acarosporaceae k:Fungi
STEP 4. FUNGuilds Assignment
We can also assign Fungi Functional Guilds for each taxonomy using FUNGuilds.
if [ ! -f $BASE.guilds.txt ]; then
amptk funguild -i $BASE.cluster.otu_table.taxonomy.txt --db fungi -o $BASE
fi
Checking AMPtkITS.guilds.txt result
cut -f11 AMPtkITS.guilds.txt | sort | uniq -c
60 -
2 Animal Endosymbiont-Animal Pathogen-Endophyte-Plant Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph
2 Animal Pathogen-Endophyte-Plant Pathogen-Wood Saprotroph
1 Animal Pathogen-Fungal Parasite-Undefined Saprotroph
1 Animal Pathogen-Plant Pathogen-Soil Saprotroph-Undefined Saprotroph
5 Animal Pathogen-Plant Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph
1 Animal Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph
1 Dung Saprotroph-Plant Saprotroph
1 Ectomycorrhizal-Fungal Parasite-Plant Pathogen-Wood Saprotroph
1 Fungal Parasite-Plant Pathogen-Plant Saprotroph
7 Fungal Parasite-Undefined Saprotroph
1 Guild
15 Lichenized
2 Plant Pathogen
10 Undefined Saprotroph
STEP 5. Run 01_AMPtk_ITS.sh
We’ve learned all four main steps for NGS amplicon data processing. Now, we will add all the steps together and run as a bash script 01_AMPtk_ITS.sh
sbatch pipeline/01_AMPtk_ITS.sh
We only process 5 samples. AMPtk will take several minutes. When the run is completed, you should generate these files.
ls -ltr
total 55296
drwxr-xr-x 2 npomb001 stajichlab 4096 Sep 11 08:44 pipeline
drwxr-xr-x 2 npomb001 stajichlab 4096 Sep 11 08:44 logs
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 28 Sep 11 11:30 AMPtkITS.filenames.txt
drwxr-xr-x 2 npomb001 stajichlab 4096 Sep 11 11:31 AMPtkITS
drwxr-xr-x 2 npomb001 stajichlab 4096 Sep 11 11:31 illumina
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 595 Sep 11 11:31 AMPtkITS.mapping_file.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 51554828 Sep 11 11:32 AMPtkITS.demux.fq.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 15232 Sep 11 11:32 AMPtkITS.amptk-demux.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 6841 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.amptk-cluster.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 24994 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.otus.fa
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 1948 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.otu_table.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 12158 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.otu_table.taxonomy.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 35195 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.otus.taxonomy.fa
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 27614 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.taxonomy.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 3474 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.tree.phy
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 17638 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.biom
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 5384 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.cluster.amptk-taxonomy.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 npomb001 stajichlab 25045 Sep 11 11:35 AMPtkITS.guilds.txt